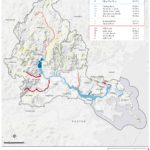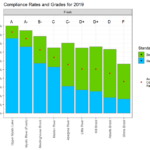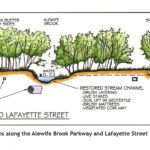
By Kristin Anderson and David White We are at an important point in the history of the Alewife Brook. The Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA) and the cities of Cambridge and Somerville are preparing a new long-term sewage control plan for the Alewife Brook/Upper Mystic River Watershed. Climate change, with its wetter rainy season, more intense storms, and sea level rise, is expected to result in more hazardous Alewife Brook sewage pollution and more flooding in the area. During some storms, the Alewife Brook floods into the houses, parks, and yards of area residents in environmental justice communities. Because of [READ MORE]