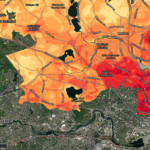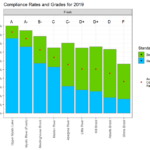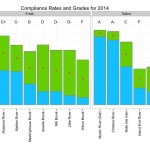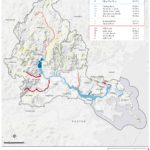
By Meg Muckenhoupt In 1972, the Clean Water Act called for all waterways to be “fishable and swimmable” by 1983, and for all pollution discharges to end by 1985. That still hasn’t happened, as is shown by the new annual water quality report card issued by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for the Mystic River in July. All of Belmont’s brooks received a D or D+ grade because they failed to meet state E. coli bacteria standards for boating in 45% to 55% of samples taken in 2021. Site 2021 2014 Grade Total Grade Total Alewife Brook D 47% D [READ MORE]