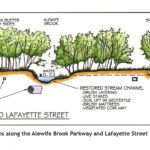
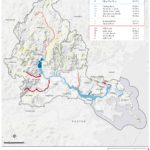
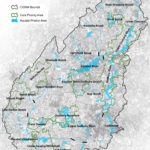
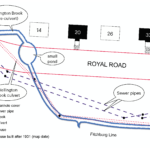
by Jean Devine An open mind, eagerness to learn new things, a willingness to work with peers from different schools, and a tolerance for hot weather, a bit of rain, and getting dirty are all it takes to be a Biodiversity Builder. Youth don’t join Biodiversity Builders (BB) to fill out their resume. They join because they’re curious about nature and maybe gardening, they worry about climate change, and they want to do something positive to help the planet. Youth who become Biodiversity Builders learn how to solve environmental and societal challenges, get down and dirty removing invasive plants and [READ MORE]